In the last couple of decades, industries have been steadily migrating from traditional on-premises IT to cloud infrastructures. This gradual shift accelerated during the COVID-19 pandemic, as businesses sought secure, efficient, reliable, and scalable ways to enable remote work. So what characteristics of cloud computing are pushing businesses to make that shift?
Well, obviously, security, efficiency, reliability, and scalability are among them. However, they’re not the only ones. We’ll discuss each of those cloud characteristics and several more shortly. But before we do that, let’s have a brief introduction on cloud computing.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of various IT-related services such as compute, storage, analytics, and applications, through the Internet in an on-demand, self-service manner. Underneath those services are pooled computing resources that have been virtualized so that they could be shared among multiple tenants.
That was just a brief introductory definition, so don’t worry if it raised more questions instead. You’ll get a better understanding of cloud computing once you’ve gone through all the cloud characteristics we’ve outlined below, so let’s get the ball rolling.
1. Utilizes Resource Pooling
One of the major features of cloud computing is its utilization of resource pooling. It’s a practice wherein a cloud service provider’s array of computing resources such as CPU, memory, network bandwidth, and storage are pooled together and then delivered to consumers in a multi-tenant environment.
Resource pooling offers two major benefits. It maximizes resource utilization and improves resiliency against individual component failures. Allow me to elaborate a bit on what I mean by these.
Maximizes resource utilization
Pooled resources can be dynamically allocated to cloud service consumers (tenants) on an as-needed basis. If a consumer doesn’t need a set of resources at a given period, those resources can be reallocated to another consumer who needs it.
One particular scenario where this can happen is when consumers belong to different industries or time zones and, hence, have different usage peaks or usage patterns. Because resources can be reallocated dynamically, more consumers can be served by a pooled system than an un-pooled system given the same amount of resources.
Improves resiliency against individual component failures
Cloud service consumers are abstracted from the underlying physical resources comprising a resource pool. Thus, even if a resource, say a processor—heck, even an entire physical server—fails, the cloud infrastructure will make adjustments so that healthy resources can continue providing the service.
2. Enables On-Demand and Self-Service Functionality
Cloud users can provision as well as deploy servers and applications on their own, i.e., in a ‘self-service’ manner. You don’t have this level of autonomy in traditional IT environments, where IT admins have to wait for procurement/purchasing officers to acquire the physical servers, and users have to wait for IT admins to provision and deploy the configured servers before they can proceed with their tasks.
Moreover, cloud users can do so whenever the need arises. In other words, they can launch a server instance or any cloud resource on-demand. The on-demand and self-service capabilities of the cloud are highly beneficial to users, IT admins, and business leaders because it allows you to do away with all the bureaucratic red tape that delays several IT processes. It also frees up time for individuals normally involved in these processes.
3. Provides Broad Network Access
Cloud computing services are accessible through the Web. Given the Internet’s widespread support from a broad range of network providers, including traditional fixed-line Internet Service Providers (ISPs), cable TV network providers, telecommunications companies, and recently even satellite constellations (e.g. Starlink), that means cloud services are virtually accessible from almost anywhere.
That also means cloud services can be accessed from almost any endpoint device, including PCs, laptops, thin clients, smartphones, and tablets. This broad network access capability makes cloud computing the perfect fit if you’re operating across the globe or across geographical regions, or if you need to support remote workers.
4. Simplifies Maintenance Tasks
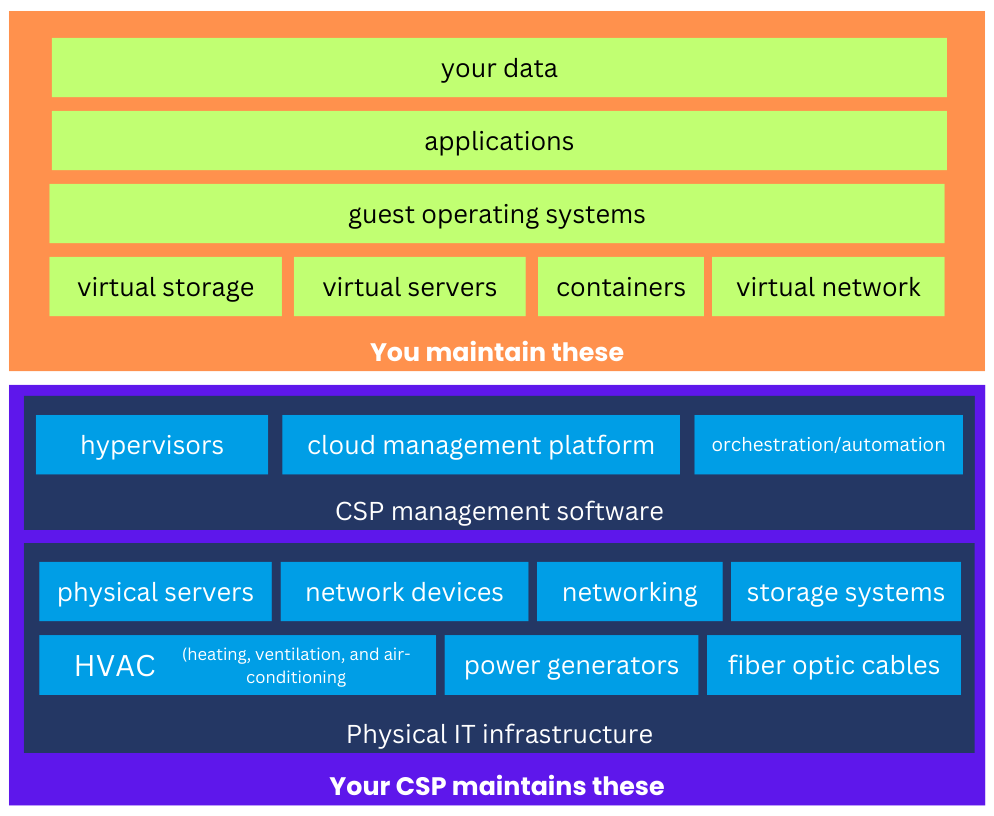
When you migrate your IT infrastructure to the cloud, you no longer have to worry about the underlying physical infrastructure. No need to maintain physical servers, routers, switches, storage systems, or the physical network. If you’re used to running your IT infrastructure from an on-premises data center, you don’t have to maintain racks, cooling systems, and power generators either.
Everything you need to manage and maintain are presented in software form and, in most cases, can be administered from a single administrative interface. And since this administrative interface is also hosted in the cloud, you can carry out management and maintenance tasks from practically anywhere.
5. Drives Scalability And Rapid Elasticity
Provisioning and deploying a cloud-based virtual server instance is fast and easy. You can do it with just a few clicks and in just a couple of minutes. And then once you have a clone a.k.a. an image of that instance, you can create new instances off of that image. This will allow you to quickly scale up your infrastructure. You can also scale down as quickly by simply terminating those instances.
You can even scale your infrastructure automatically if you leverage certain cloud services like auto-scaling. An auto-scaling service will monitor your server instances and then launch or terminate instances based on demand. The scalability and rapid elasticity of cloud environments make them suitable for seasonal demand or for rapidly growing businesses.
6. Cost Effective
As you might have gathered from the previous sections, cloud computing enables IT admins to accomplish tasks much faster. What would usually take days, weeks, or months to complete can now be done in just a matter of hours or sometimes even minutes.
Sure, there are operational costs that have to be addressed, as you still need to pay for the cloud resources you consume. However, considering how much you’re able to accomplish in a significantly shorter period of time, cloud computing is very cost effective. You truly get your money’s worth.
7. Delivers Measured Service And Detailed Reporting
Most cloud services are billed based on actual usage. So, for example, if you use a particular server instance for, say, 50 hours, then you’ll only be billed for that consumption. The concept is similar to the measured services (a.k.a. metered services) of public utilities such as electricity and water, except that cloud services collect a substantially greater amount of data.
All that telemetry can help inform decision making. The sizable amount of usage data gathered allows cloud service providers (CSPs) to generate detailed reports about your consumption. So, you can, for example, drill down a report to view the daily usage of a specific server instance or the monthly usage of each instance type.
These detailed reports are important because, although cloud computing lets you save on upfront costs, its ongoing costs can rapidly escalate if you don’t monitor and manage them properly. You need to exercise proper cloud cost management and optimization for your cloud adoption endeavors to succeed. Detailed reports can be a big help in that regard.
8. Highly Secure
One of the perceived challenges of cloud computing is security or the lack thereof. This is a misconception. Cloud environments are actually highly secure, especially if you’re talking about those operated by the large CSPs such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. These large CSPs are able to leverage economies of scale to deploy enterprise-grade security to the underlying data center facilities themselves, all the way up to the cloud services that you directly interact with.
Your CSP will often provide you with their own selection of security services. This usually includes data-at-rest and data-in-motion encryption, key management, identity and access control, and DDoS protection, among many others. But in addition to these CSP-provided services, you can also purchase additional security services from your CSP’s partner network to enhance or augment your defenses.
9. Enables Automation
A major reason why cloud environments are highly scalable and cost-efficient is because many of the processes can be automated. Usually, your CSP will provide tools that can help you automate various IT operations.
Cloud environments also enable you to manage your IT infrastructure through scripts and configuration files through what is known as Infrastructure as Code (IaC). By automating IT infrastructure management through IaC, you can gain speed, consistency, efficiency and accountability (because you can apply version control to configuration files) while decreasing costs.
10. Enhances Resiliency And Availability
When talking about IT infrastructure, resiliency refers to an infrastructure’s ability to recover quickly from a disruption. Availability, on the other hand, is a measurement of an infrastructure’s ability to remain accessible to users over a period of one year. This measurement is typically expressed in percentages such as 99% (3.65 days of downtime), 99.9% (8.76 hours of downtime), 99.99% (50 minutes of downtime), and 99.999% (5 minutes of downtime).
Due to their scalability and automation capabilities, cloud environments enable you to easily apply redundancy throughout your IT infrastructure. Redundancy is a crucial building block in highly resilient and highly available infrastructures because it provides active components a means to failover in case they become overloaded or encounter issues.
11. Enables Users To Work From Any Location
One of the major advantages of cloud computing’s ability to provide broad network access is that it then allows users to work from any location. As long as you’re using a device with Internet connectivity, you should be able to connect to a cloud-based service.
This capability was in full display at the height of the pandemic, when companies were forced to send many of their employees home. Several businesses were able to remain operational by giving employees access to cloud-hosted, company-managed Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications or Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) virtual desktops and applications.
12. Supports Multi-Tenancy
Cloud environments are multi-tenant by design. For private clouds, that means business units from the same organization share the underlying infrastructure. For public clouds, it’s customers (which consist of different organizations) that share the underlying infrastructure.
The multi-tenant nature of cloud environments is one of the reasons why some businesses prefer private clouds over public clouds. They fear that if a data leak happens, their data could end up with another company. While this is a valid concern, most CSPs already institute multiple logical separation mechanisms such as virtual private clouds, host isolation, and instance isolation, to minimize the risk of a data leak.
13. Promotes Service Excellence
CSPs are bound by service level agreements (SLAs) that ensure they maintain a minimum level of quality and availability for their cloud services. Most of these levels—e.g. 99.99% availability and 99.999% availability—are exceptionally high.
Thus, if you deliver an application hosted in the cloud, you can take advantage of these levels of availability and pass them on to your own end users. Both you and your end users can then use these services with very minimal downtime.
14. Provides A Comfortable Payment Structure
Cloud services often follow a pay-as-you-go or consumption-based payment structure. In this OPEX-based structure, you only pay for the resources you use. It’s very different from the CAPEX-based model of traditional IT, where you have to acquire your IT equipment first and, consequently, pay a huge upfront cost. In cloud computing architecture, the upfront cost is practically zero.
This flexible payment scheme can level the playing field for small and medium-sized businesses that wish to leverage but can’t afford the upfront costs of enterprise-grade IT infrastructure. It’s also ideal for businesses operating in seasonal industries where computing demand ebbs and flows. If you’re running a business that only requires high computing capacity once a year, you wouldn’t want to pay for maximum capacity the rest of the year, would you? Only cloud computing will allow you to do that.
Final Words
Since you’ve reached this far, it should be safe to assume you’re really not very familiar with cloud computing yet—at least before reading this post. I only hope the 14 characteristics of cloud computing we shared here have given you enough knowledge to appreciate the value this technology brings to businesses.
That said, I’m sure there were a few terms in the article that were also new to you. You might find some of them in the Frequently Asked Questions section below.
FAQ
What is version control?
Version control is a mechanism in software development that involves tracking changes to code. It allows you to give developers immediate feedback, deploy applications more frequently, improve application reliability, and—because file changes are attributed to the developer who made the change—establish developer accountability. You can also apply version control when employing IaC in cloud-based IT infrastructure management processes.
What is Infrastructure as Code?
Infrastructure as Code or IaC is the process of automating IT infrastructure management by using configuration files. IaC makes management faster and easier because if you want to make changes to a target environment in your IT infrastructure, you can simply apply changes to the configuration files instead of doing it manually on the target environment itself.
What is Cloud Cost Management?
Cloud cost management is the process of monitoring, analyzing, and controlling costs associated with cloud services usage. It’s a critical part of cloud adoption because, without it, your cloud usage costs can quickly get out of hand. There are CSP-provided tools as well as third party tools to help you manage your costs. However, in some cases, you might want to hire a professional to do the nitty gritty stuff for you.
What is SaaS?
SaaS or Software as a Service is one of three major types of cloud computing services. The other two being Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS). Among the three, SaaS requires the least amount of IT administration and is usually geared towards end users.
What is VDI?
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure or VDI is a virtualization solution that delivers virtualized applications and desktops from a central location to various endpoint devices. VDI applications and desktops can be delivered remotely to PCs, laptops, phones, tablets, and thin clients.